From Idea to Prototype in Just 5 Days — The Performix Design Sprint Way
Product Design Sprint Services
Accelerate Innovation and Validate Business Ideas with Performix
At Performix, our Product Design Sprint services help you rapidly move from concept to validated prototype. Using Google’s proven Design Sprint framework, we condense months of product strategy, user research, and design into an intense 5-day innovation process — empowering your business to make data-driven decisions, minimize risks, and accelerate product development.
Book a Free Discovery Call and see how a Design Sprint can transform your idea into a tested, ready-to-build solution.
Why Choose a Product Design Sprint?
Reduce Uncertainty. Validate Early. Build Smarter.
In today’s fast-paced digital ecosystem, speed and validation are everything. The Performix Design Sprint is a focused, user-centered process that enables teams to test ideas, validate assumptions, and deliver business value — faster than traditional product development cycles.
Key Benefits of a Design Sprint
Rapid 5-Day Process
User-Centered Design
Aligned Collaboration
Early Risk Mitigation
Innovation and Creativity
Clear Direction
Faster Time-to-Market
Why Performix for Design Sprint?
At Performix, we combine creativity with technical precision to deliver Design Sprints that are strategic, actionable, and user-driven.
Our team of product strategists, UX designers, and developers ensures every sprint delivers tangible results — not just concepts.
What Sets Us Apart
Experienced product design and development team
Deep understanding of startup and enterprise innovation needs
Proven results in SaaS, eCommerce, FinTech, and HealthTech
Agile and collaborative sprint methodology
Transparent communication and measurable outcomes
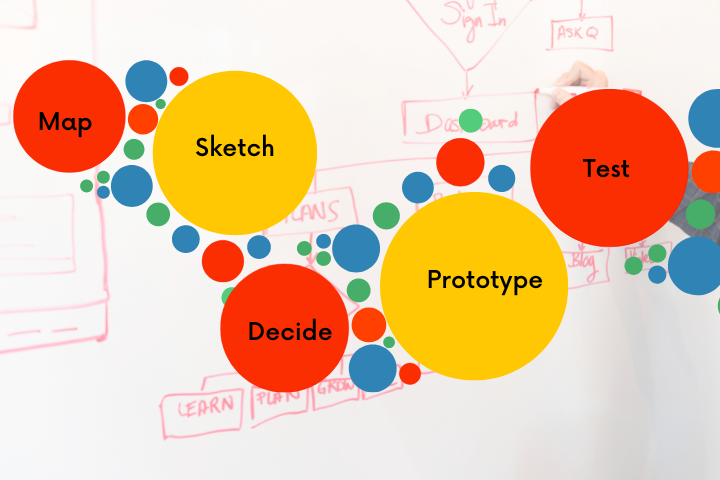
The 5-Day Performix Design Sprint Framework
A Proven Process for Fast Innovation and Real Results
Our structured Design Sprint methodology is based on proven Agile and Design Thinking principles, helping teams answer critical business questions through rapid prototyping and testing.
Day 1: Discovery Monday — Understand & Define the Problem
Day 2: Conceptualize Tuesday — Ideate & Visualize
Day 3: Decision Wednesday — Select & Prioritize
Day 4: Prototype Thursday — Build & Bring Ideas to Life
Day 5: Feedback Friday — Test, Learn & Refine

Transform Your Product Ideas into Reality
Whether you’re a startup validating a new idea or an enterprise innovating your next big product, our Product Design Sprint helps you make confident, data-backed decisions before development.
Transform your vision into a validated prototype in just 5 days with Performix.
Let’s innovate faster, smarter, and with clarity.
Get Started Today

Frequently Asked Questions
Jake Knapp and Google Ventures UX professionals devised the 5-day Design Sprint. During a Create Sprint, we share ideas, outline solutions, and design interfaces to develop a clickable prototype.
Design Sprint validates possible solutions in days with actual consumers. A clickable prototype is produced by the end of the week during a Sprint. Understand, diverge, converge, prototype, and test to obtain solutions.
Design Thinking made the Design Sprint possible. Stanford University in Silicon Valley introduced Design Thinking. Tom & David Kelley formed the product-design business IDEO. They developed multidisciplinary teams (ethnologists, designers, marketers, etc.) to address issues or build breakthrough solutions.
Design thinking has five stages:
- User context empathy
- Define problems
- Imagine solutions
- Create interesting prototypes
- Test with real users to enhance the product.
Design Thinking is more of a theory than a real "out-of-the-box" strategy, hence firms struggle to implement it. This is Design Sprint's value.
The Design Sprint has a defined path and distinct exercises. The workdays are rhythmic and fast-paced. At the end of a Sprint, prototypes or test movies might be shown to internal and external partners. The design sprint leader will maximize the 5 days' ROI.
The Design Sprint makes Design Thinking practical.
Design Sprint and Hackathon are philosophically similar in that they both describe methods for discovering innovative solutions to a given challenge within a restricted amount of time and space.
Hackathons have become popular events whose primary purpose is not to solve a problem but rather to network. The majority of Hackathons are organized by large corporations for promotional or talent acquisition goals.
Design Sprints are perfect when you have a preliminary idea for a new product, an existing product you want to improve, or you want to go beyond essential functionality and add additional features. A Design Sprint helps Startups and Enterprises identify process gaps and barriers.
